What Are the Environmental Impacts of Irrigation in Saudi Arabia
13 August, 2024
Introduction
Irrigation is a critical practice in agriculture, especially in arid and semi-arid regions like Saudi Arabia. As one of the world’s most water-scarce countries, Saudi Arabia relies heavily on irrigation to sustain its agricultural sector and ensure food security. However, the environmental impacts of irrigation in this region are complex and multifaceted. This article delves into the environmental consequences of irrigation in Saudi Arabia, focusing on the challenges and solutions associated with Irrigation Installation in Saudi Arabia.
I. The Role of Irrigation in Saudi Arabia
1.1 Historical Context
Saudi Arabia's arid climate presents significant challenges for agriculture. Historically, traditional irrigation methods such as qanats and wells were employed to support farming activities. However, the discovery of oil in the 20th century and subsequent economic growth led to an expansion of irrigation infrastructure.
1.2 Modern Irrigation Techniques
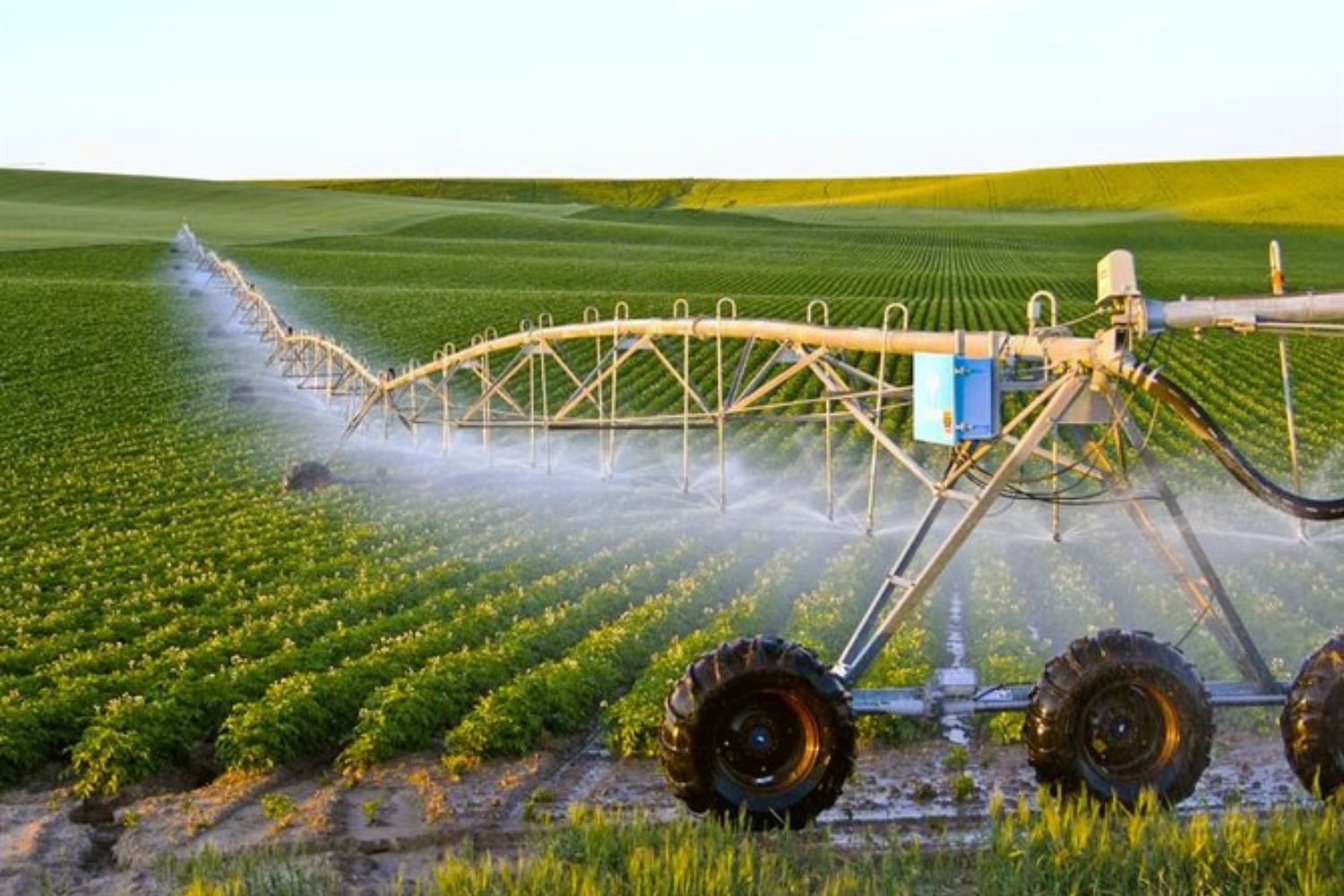
Today, modern irrigation techniques such as drip irrigation, center pivot irrigation, and sprinkler systems are prevalent. These methods are designed to maximize water efficiency and crop yield. The adoption of advanced irrigation technologies has transformed agriculture in Saudi Arabia, allowing the cultivation of various crops in otherwise inhospitable conditions.
II. Water Resource Depletion
2.1 Over-extraction of Groundwater
One of the most pressing environmental impacts of irrigation in Saudi Arabia is the over-extraction of groundwater. The country's reliance on fossil aquifers, which are not replenished by natural processes, has led to a significant decline in groundwater levels. This depletion affects not only agricultural productivity but also the availability of water for other uses.
2.2 Impact on Aquifer Systems
The over-extraction of groundwater has led to the degradation of aquifer systems. Aquifer depletion can result in land subsidence, where the ground sinks due to the collapse of underground water reservoirs. This phenomenon has been observed in various parts of Saudi Arabia and poses a threat to infrastructure and agricultural lands.
III. Soil Salinization
3.1 Causes of Soil Salinization
Soil salinization is a major concern in irrigated areas of Saudi Arabia. The accumulation of salts in the soil is primarily caused by the use of saline water for irrigation, inadequate drainage systems, and the evaporation of water from the soil surface. As irrigation water evaporates, it leaves behind salts that accumulate in the soil, reducing its fertility and affecting crop growth.
3.2 Consequences for Agriculture
Salinized soil negatively impacts agricultural productivity. High salt concentrations can inhibit plant growth, reduce crop yields, and diminish soil quality. Farmers may need to invest in soil reclamation techniques, which can be costly and environmentally taxing.
IV. Environmental Impact on Ecosystems
4.1 Alteration of Natural Landscapes
The installation of irrigation systems often involves significant land modification, such as the creation of irrigation canals and reservoirs. This alteration of natural landscapes can disrupt local ecosystems and biodiversity. For instance, the transformation of desert land into arable farmland can lead to the displacement of native flora and fauna.
4.2 Water Usage and Ecosystems
The diversion of water for irrigation can affect natural water bodies and ecosystems. Reduced flow in rivers and wetlands can impact aquatic life and alter the natural balance of ecosystems. Additionally, the creation of artificial water bodies can sometimes lead to the introduction of non-native species, further disrupting local ecosystems.
V. Energy Consumption
5.1 Energy Requirements for Irrigation
The irrigation process, especially when utilizing advanced technologies such as drip irrigation and center pivots, requires substantial energy. This energy is often derived from fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The reliance on energy-intensive irrigation systems can exacerbate the environmental impact of agriculture in Saudi Arabia.
5.2 Renewable Energy Solutions
To mitigate the environmental impact of energy consumption, there is a growing interest in integrating renewable energy sources into irrigation systems. Solar-powered irrigation systems are one such solution, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources.
VI. Strategies for Sustainable Irrigation
6.1 Efficient Irrigation Technologies
The adoption of efficient irrigation technologies is crucial for minimizing environmental impacts. Drip irrigation, for instance, delivers water directly to the plant roots, reducing water wastage and improving efficiency. Similarly, precision irrigation systems can optimize water use based on soil moisture levels and crop needs.
6.2 Water Recycling and Reuse
Water recycling and reuse are essential strategies for sustainable irrigation. Techniques such as rainwater harvesting and the treatment of wastewater for agricultural use can reduce reliance on freshwater resources and mitigate environmental impacts.
6.3 Soil Management Practices
Implementing soil management practices can help combat soil salinization and maintain soil health. Practices such as soil conditioning, the use of organic fertilizers, and proper drainage can improve soil fertility and reduce salinity levels.
6.4 Policy and Regulation
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in promoting sustainable irrigation practices. Policies that encourage water conservation, regulate groundwater extraction, and support the adoption of efficient irrigation technologies can contribute to environmental sustainability.
VII. Case Studies and Success Stories
7.1 Innovative Projects in Saudi Arabia
Several innovative irrigation projects in Saudi Arabia serve as models for sustainable practices. For example, the King Abdullah Initiative for Saudi Agricultural Investment Abroad aims to enhance food security through sustainable agricultural practices and water management.
7.2 International Collaborations
Collaborations with international organizations and experts can provide valuable insights and support for sustainable irrigation practices. Initiatives such as the Saudi Green Initiative focus on environmental sustainability and aim to address challenges related to water and agriculture.
VIII. Conclusion
The environmental impacts of irrigation in Saudi Arabia are multifaceted, involving challenges such as water resource depletion, soil salinization, ecosystem disruption, and energy consumption. However, by adopting efficient irrigation technologies, implementing sustainable practices, and supporting policy initiatives, it is possible to mitigate these impacts and promote environmental sustainability.
As Saudi Arabia continues to invest in irrigation infrastructure, the focus must be on balancing agricultural productivity with environmental conservation. Innovations in irrigation installation and water management, coupled with strategic policies, can help ensure that Saudi Arabia's agricultural sector remains both productive and environmentally responsible.
IX. Future Directions
9.1 Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are essential for advancing sustainable irrigation practices. Investing in new technologies, improving water management strategies, and exploring innovative solutions can help address the environmental challenges associated with irrigation.
9.2 Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the environmental impacts of irrigation and the importance of sustainable practices is crucial. Education programs and community engagement can foster a culture of conservation and encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly irrigation techniques.
By addressing these key areas, Saudi Arabia can work towards a more sustainable and resilient agricultural sector that supports both economic growth and environmental preservation.
- Fountain and Waterfalls
- Gardening
- hardscape
- Irrigation system
- Landscape
- Lawn
- Nursery
- Palm Tree
- Plantation and Maintenance
- softscape
- Tree Transplanting
- Washingtonian Tree
Categories
Latest Post
- Fountain and Waterfalls
- Gardening
- hardscape
- Irrigation system
- Landscape
- Lawn
- Nursery
- Palm Tree
- Plantation and Maintenance
- softscape
- Tree Transplanting
- Washingtonian Tree





 .
.


























































































